Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Tutorial 1 - Creating a Model
This tutorial shows how to create a simple finite element model from scratch
The preparation stage
Before building a model, we need to load the used components.
Every model needs one System instance. Furthermore,
we are going to use several Node and Element instances.
Loading those class definitions requires the following:
from femedu.domain import System, Node
from femedu.elements.linear import Truss
from femedu.materials import ElasticSection
The first line imports the System and Node class definitions,
the second line imports the Truss from the linear package, i.e., the
small deformation finite element on variational base.
Start by creating a System instance.
model = System()
The model object will hold all information forming your finite element model, as well as provide the interface for analysis control, plotting, and data gathering.
Next, we are creating nodes as Node objects.
nd0 = Node( 0.0, 0.0)
nd1 = Node( 8.0, 6.0)
nd2 = Node(16.0, 0.0)
It is important to understand that nd0, nd1, nd2 are instances of Node and provide
a permanent pointer to those nodes and all their information throughout the entire analysis. We will
use those pointers to collect data or make control decisions.
We also need to add those node objects to our model.
model.addNode(nd0, nd1, nd2)
nodes can be added one at a time or, as shown above, as a group of nodes.
Every node holds information about
Type |
Description |
Access through |
|---|---|---|
Position |
initial coordinates of the node |
getPos() |
Displacement |
current displacement components |
getDisp([‘ux’, …]) |
Attached elements |
Pointers to all connected elements |
internal |
Available dofs |
Union of dofs used by any of the attached elements |
internal |
Index for a dof |
Global index for locating each nodal dof in system arrays. |
getIdx4DOFs(dof-list) |
Index for one attached element |
Global index array for locating element-specific dofs in system arrays. |
getIdx4Element(elem) |
Once nodes have been created, we can create and add elements to the model. This can be done by creating an element as
# define material parameters
params = dict(
E = 1000., # Young's modulus
A = 1.0, # cross section area
)
elem0 = Truss(nd0, nd1, ElasticSection(params))
and adding that element to the model using
model.addElement(elem0)
or by creating and adding elements in one single step
model.addElement(Truss(nd1, nd2, ElasticSection(params)))
The first option allows us to keep elem0 as element pointer for later access to that element. The second option is sufficient in most cases.
FEM.edu also provides a short version for the addElement() function in the form
model += Truss(nd0, nd2, ElasticSection(params))
Note
In FEM.edu, every material instance holds information about the current state of the material, including strain, stress, plastic strain, hardening parameters, and more. Since these are private to any particular material point, each element requires its own material instance.
Creating one instance of AnyMaterial(params)() and handing that instance
to the element constructor will most likely lead to a faulty model.
Geometric boundary conditions are applied at nodes. In order to add a geometric boundary condition to a node,
we need to use the node pointer, i.e., the variable holding the Node instance.
In this example, we shall model nd0 as fixed and nd2 as a horizontal roller.
nd0.fixDOF(['ux','uy']) # pin
nd2.fixDOF(['uy']) # horizontal roller
FEM.edu always identifies degrees of freedom (dofs) using a short name string. Several dofs are predefined and used by the standard elements, though user elements and user algorithms may define additional variables as long as their respective name remains unique. Built-in standard dofs are shown in the following table.
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
ux |
component of displacement in the x-direction |
uy |
component of displacement in the y-direction |
uz |
component of displacement in the z-direction |
rx |
component of (linearized) rotation about the x-axis |
ry |
component of (linearized) rotation about the y-axis |
rz |
component of (linearized) rotation about the z-axis |
Now we are ready to load the model. This example shall be limited to simple nodal loads. For examples of more complex load patters refer to Tutorial 2 - Using Meshers
nd1.addLoad([-1.0],['uy'])
We may want to review the model status before engaging in any analysis. The easiest way is to request a report about the current state of the model as follows.
Warning
A call to model.report() may result in a lot of output if you are working on a large model.
model.report()
System Analysis Report
=======================
Nodes:
---------------------
Node_4844:
x: [0.000 0.000]
fix: ['ux', 'uy']
u: None
Node_4845:
x: [8.000 6.000]
P: [0.000 -1.000]
u: None
Node_4846:
x: [16.000 0.000]
fix: ['uy']
u: None
Elements:
---------------------
Truss: Node_4844 to Node_4845:
material properties: ElasticSection(Material)({'E': 1000.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30, 'I': 1.0}) strain:{'axial': 0.0, 'flexure': 0.0} stress:{'axial': 0.0, 'flexure': 0.0}
internal force: 0.0
Truss: Node_4845 to Node_4846:
material properties: ElasticSection(Material)({'E': 1000.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30, 'I': 1.0}) strain:{'axial': 0.0, 'flexure': 0.0} stress:{'axial': 0.0, 'flexure': 0.0}
internal force: 0.0
Truss: Node_4844 to Node_4846:
material properties: ElasticSection(Material)({'E': 1000.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30, 'I': 1.0}) strain:{'axial': 0.0, 'flexure': 0.0} stress:{'axial': 0.0, 'flexure': 0.0}
internal force: 0.0
Things to note in this report:
FEM.edu assigns unique names to nodes and elements. These are mostly internal identifiers but may be used by the user when analyzing/debugging program output. It is recommended to use your own node and element references to access node and element data.
Nodes always report their reference position, but will also report fixed dofs or applied nodal loads if either was assigned to a node.
Once an analysis has been performed, nodes will also show their current state of displacement.
Another easy validation of your input can be obtained using the built-in system plot.
#model.resetDisp()
model.plot(factor=0.0,
title="Tutorial 1: Undeformed System",
show_bc=True, show_loads=True, show_reactions=False)
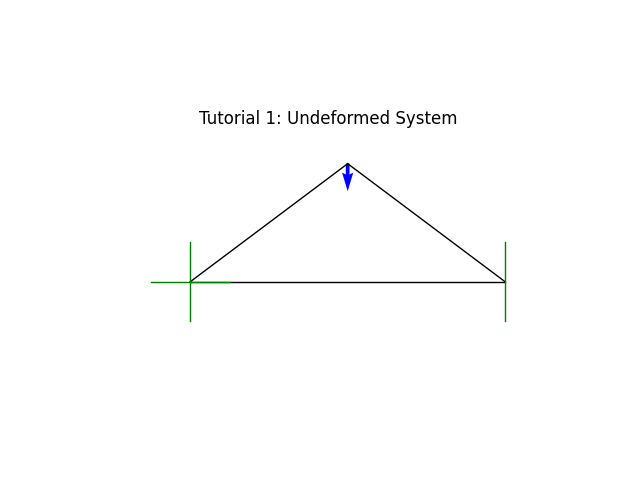
At this point we are ready for the analysis.
Since this is a linear model, we will use the default solver, which is a LinearSolver object.
All we need to perform the analysis is
model.solve()
At this point, we may just plot the deformed system
model.plot(factor=25.0,
title="Tutorial 1: Deformed System (factor=25.0)",
filename="tutorial01_deformed.png",
show_loads=True, show_reactions=True)
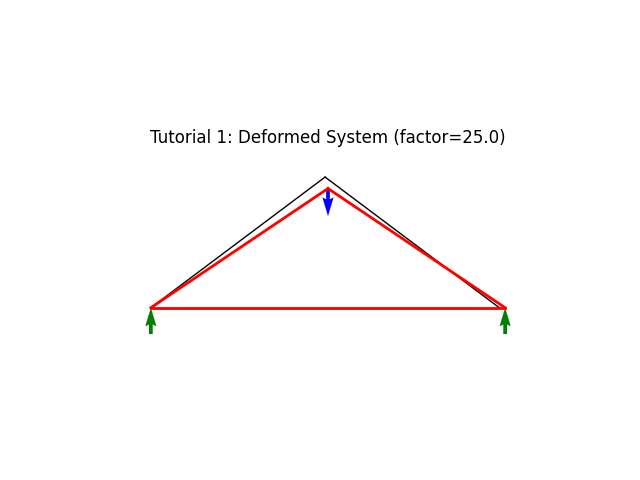
Note
Providing the filename= option will save the generated figure a file with the given name. The name may include a full path, specifying a destination folder and filename. If no path is given, the figure file will be saved to the current runtime folder.
The image file type is determined from the extension in the filename option. It is recommended to used “.pdf” for best quality (vector graphics for use in publications) or “.png” for web presentation. Avoid “.jpg” for line-graphics like this one.
model.report()
System Analysis Report
=======================
Nodes:
---------------------
Node_4844:
x: [0.000 0.000]
fix: ['ux', 'uy']
u: [0.000 0.000]
Node_4845:
x: [8.000 6.000]
P: [0.000 -1.000]
u: [0.005 -0.021]
Node_4846:
x: [16.000 0.000]
fix: ['uy']
u: [0.011 0.000]
Elements:
---------------------
Truss: Node_4844 to Node_4845:
material properties: ElasticSection(Material)({'E': 1000.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30, 'I': 1.0}) strain:{'axial': np.float64(-0.0008333333333333332)} stress:{'axial': np.float64(-0.8333333333333331), 'flexure': 0.0}
internal force: -0.8333333333333331
Truss: Node_4845 to Node_4846:
material properties: ElasticSection(Material)({'E': 1000.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30, 'I': 1.0}) strain:{'axial': np.float64(-0.0008333333333333332)} stress:{'axial': np.float64(-0.8333333333333331), 'flexure': 0.0}
internal force: -0.8333333333333331
Truss: Node_4844 to Node_4846:
material properties: ElasticSection(Material)({'E': 1000.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30, 'I': 1.0}) strain:{'axial': np.float64(0.0006666666666666666)} stress:{'axial': np.float64(0.6666666666666666), 'flexure': 0.0}
internal force: 0.6666666666666666
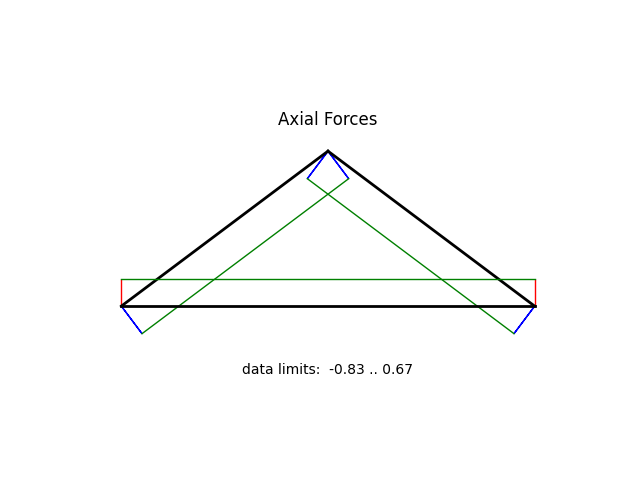
Truss, beam, and frame elements further allow for plotting of internal forces through the beamValuePlot(variable,factor=1.0,filename=’…’) method.
Valid variables are
‘F’ |
Axial force (tension positive) |
‘V’ |
transverse shear force |
‘M’ |
Bending moment |
model.beamValuePlot('F',filename='tutorial01_axial.png')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.048 seconds)