Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
A square patch made of one quadrilateral plate elements
- Basic implementation test with applied loads.
Testing the tangent stiffness computation.
free free
^ ^
| |
3-----2 -> free
| | >
| a | > (w = 1.0)
| | >
0-----1 -> free
width: 10.
height: 10.
Material parameters: St. Venant-Kirchhoff, plane stress
E = 10.0
nu = 0.30
t = 1.0
Element loads:
node 0: [ 0.0, 0.0]
node 1: [ 5.0, 0.0]
node 2: [ 5.0, 0.0]
node 3: [ 0.0, 0.0]
Author: Peter Mackenzie-Helnwein
import numpy as np
from femedu.examples import Example
from femedu.domain import System, Node
from femedu.solver import NewtonRaphsonSolver
from femedu.elements.linear import Quad
from femedu.materials import PlaneStress
class ExamplePlate07(Example):
def problem(self):
params = dict(
E = 10., # Young's modulus
nu = 0.3, # Poisson's ratio
t = 1.0, # thickness of the plate
fy = 1.e30 # yield stress
)
a = 10. # length of the plate in the x-direction
b = 10. # length of the plate in the y-direction
model = System()
model.setSolver(NewtonRaphsonSolver())
nd0 = Node( 0.0, 0.0)
nd1 = Node( a, 0.0)
nd2 = Node( a, b)
nd3 = Node( 0.0, b)
# nd0.fixDOF('ux', 'uy')
# nd1.fixDOF('uy')
# nd3.fixDOF('ux')
model.addNode(nd0, nd1, nd2, nd3)
elemA = Quad(nd0, nd1, nd2, nd3, PlaneStress(params))
model.addElement(elemA)
elemA.setSurfaceLoad(face=1, pn=1.0)
model.plot(factor=0.0, title="Undeformed system", filename="plate07_undeformed.png", show_bc=1)
# %%
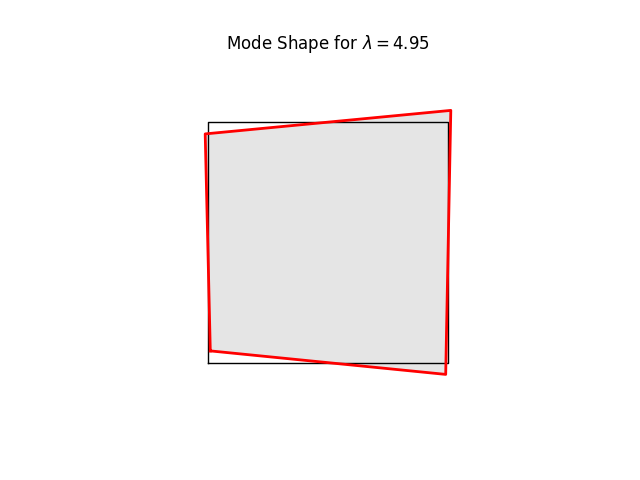
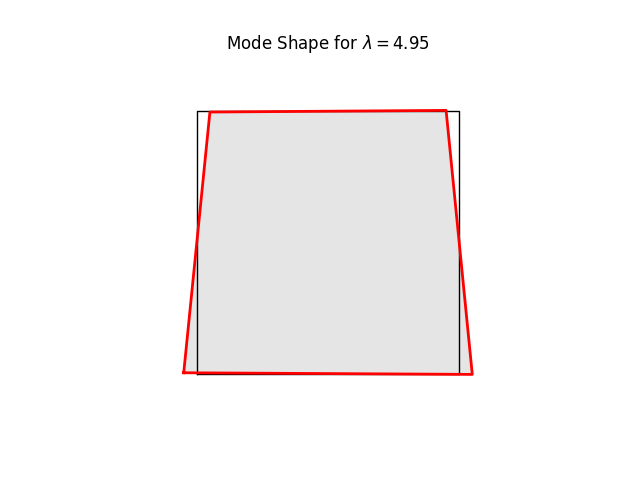
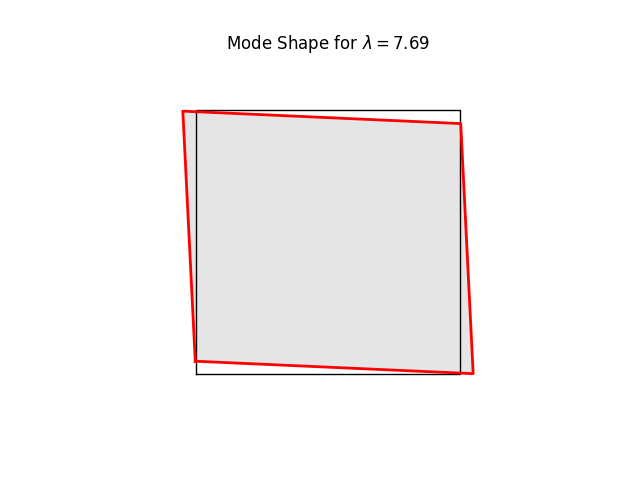
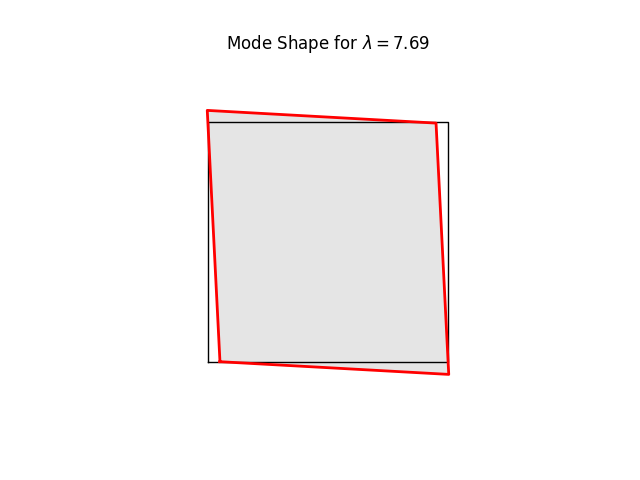
# We can have a quick look at the stiffness mode shapes using the
# buckling-mode plotter. These are simply eigenvalues and eigenvectors of Kt
# at the current load level (0.0)
#
model.setLoadFactor(0.0)
model.solve()
np.save('../../../Kplate.npy', model.solver.Kt)
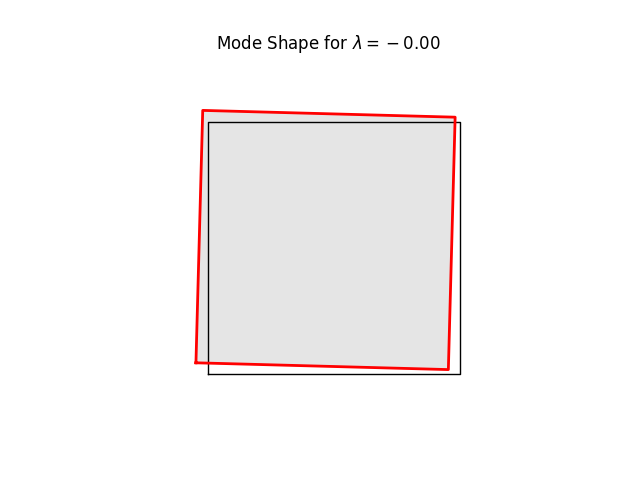
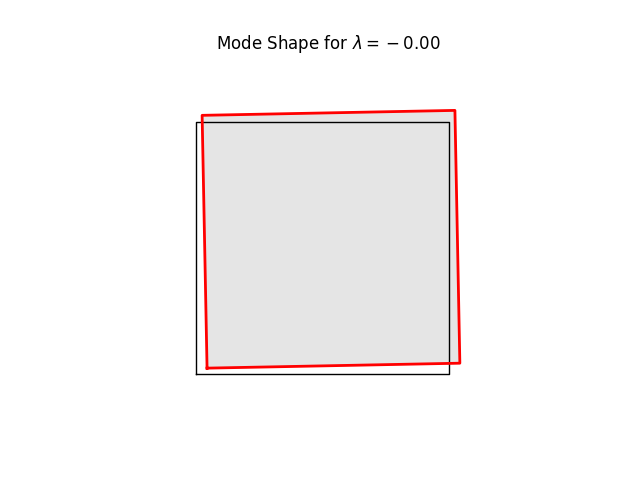
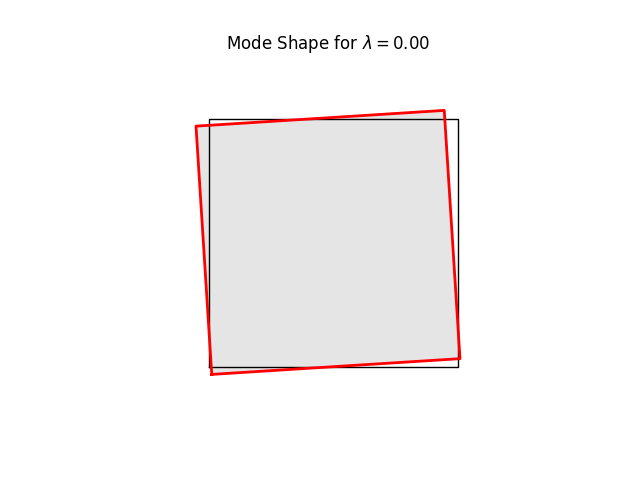
for k in range(8):
name = f"plate07_mode{k:2d}.png"
model.plotBucklingMode(mode=k,filename=name,factor=1.0)
# %%
# Note the three rigid body modes (lam=0.0). It can be shown that all three
# are limear combinations of translations in x and y-directions and a
# rigid body rotation.
#
# %%
# Now it is time to add boundary conditions, apply loads
# and check the convergence behavior.
#
nd0.fixDOF('ux', 'uy')
nd1.fixDOF('uy')
nd3.fixDOF('ux')
model.setLoadFactor(1.0)
model.solve()
# %%
# The output shows that we do have a quadratic rate of convergence.
# %%
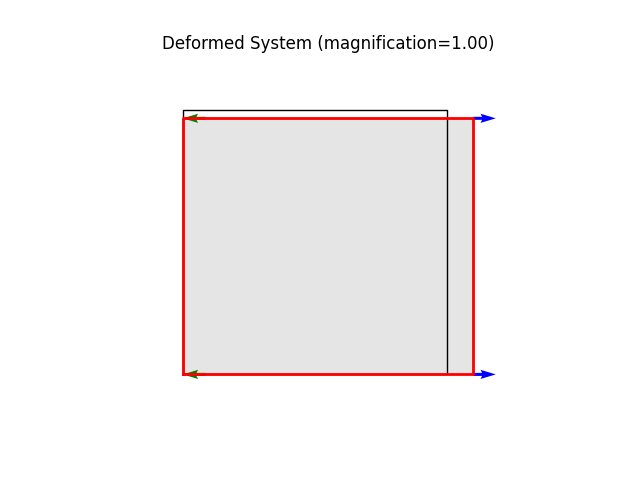
# Let's finish off with a nice plot of the deformed system.
model.plot(factor=1.0, filename="plate07_deformed.png")
model.report()
Run the example by creating an instance of the problem and executing it by calling Example.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
ex = ExamplePlate07()
ex.run()
+
+
System Analysis Report
=======================
Nodes:
---------------------
Node_1388:
x: [0. 0.]
fix: ['ux', 'uy']
u: [0. 0.]
Node_1389:
x: [10. 0.]
fix: ['uy']
u: [1. 0.]
Node_1390:
x: [10. 10.]
u: [ 1. -0.3]
Node_1391:
x: [ 0. 10.]
fix: ['ux']
u: [ 0. -0.3]
Elements:
---------------------
Quad_1803: nodes ( Node_1388 Node_1389 Node_1390 Node_1391 )
material: list
strain (0): xx=1.000e-01 yy=-3.000e-02 xy=-4.760e-18 zz=-2.100e-02
stress (0): xx=1.000e+00 yy=0.000e+00 xy=-1.831e-17 zz=0.000e+00
strain (1): xx=1.000e-01 yy=-3.000e-02 xy=8.302e-17 zz=-2.100e-02
stress (1): xx=1.000e+00 yy=0.000e+00 xy=3.193e-16 zz=0.000e+00
strain (2): xx=1.000e-01 yy=-3.000e-02 xy=-7.511e-17 zz=-2.100e-02
stress (2): xx=1.000e+00 yy=0.000e+00 xy=-2.889e-16 zz=0.000e+00
strain (3): xx=1.000e-01 yy=-3.000e-02 xy=1.857e-17 zz=-2.100e-02
stress (3): xx=1.000e+00 yy=0.000e+00 xy=7.142e-17 zz=0.000e+00
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.233 seconds)