Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Simple triangular truss.
This example is structurally identical to ExampleTruss01 but utilizes the alternative input style for adding Nodes and Elements to the model.
The system is statically determined and allows for easy validation of calculated deformation, reactions and internal forces.
Author: Peter Mackenzie-Helnwein
Setup
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from femedu.examples import Example
from femedu.domain import System, Node
from femedu.elements.linear import Truss
from femedu.materials import FiberMaterial
class ExampleTruss03(Example):
def problem(self):
# initialize a system model
B = 6.0 * 12
H = 3.0 * 12
params = {'E': 10., 'A': 1., 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1.e30}
model = System()
# create nodes
nd0 = Node(0.0, 0.0)
nd1 = Node( B, 0.0)
nd2 = Node(0.5*B, H)
model += nd0
model += nd1
model += nd2
# create elements
model += Truss(nd0, nd1, FiberMaterial(params)) # bottom 1
model += Truss(nd0, nd2, FiberMaterial(params)) # up right diag 1
model += Truss(nd1, nd2, FiberMaterial(params)) # up left diag 1
# define support(s)
nd0.fixDOF('ux') # horizontal support left end
#nd0 //= 0
nd0.fixDOF('uy') # vertical support left end
nd1.fixDOF('uy') # vertical support right end
# add loads
# .. load only the upper nodes
nd2.setLoad((0.0, -1.0), ('ux','uy'))
# analyze the model
model.solve()
# write out report
model.report()
# create plots
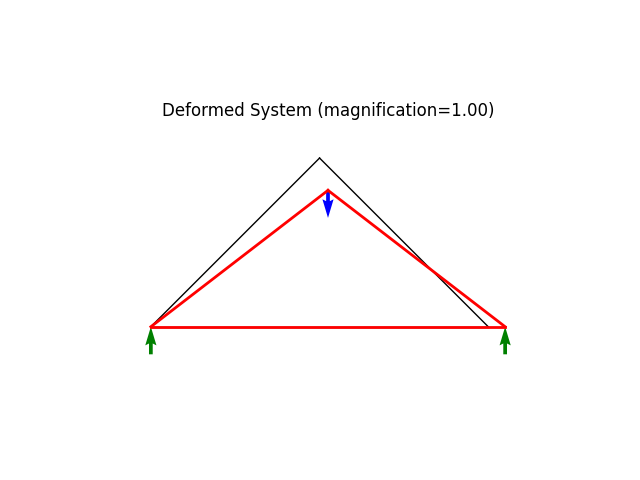
model.plot(factor=1., filename="truss03_deformed_a.png")
# fix horizontal motion of node 1
nd1.fixDOF('ux')
# add loads: same load -- nothing to do
# RE-analyze the model
model.resetDisp()
model.solve()
# skip the report
model.report()
# create plots
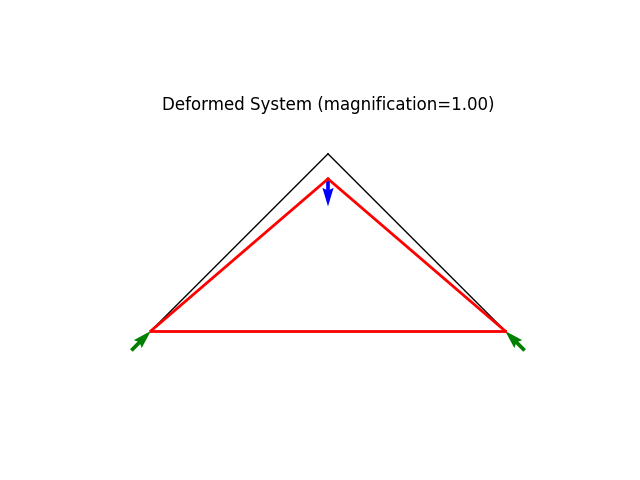
model.plot(factor=1., filename="truss03_deformed_b.png")
Run the example by creating an instance of the problem and executing it by calling Example.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
ex = ExampleTruss03()
ex.run()
System Analysis Report
=======================
Nodes:
---------------------
Node_36:
x: [0.000 0.000]
fix: ['ux', 'uy']
u: [0.000 0.000]
Node_37:
x: [72.000 0.000]
fix: ['uy']
u: [3.600 0.000]
Node_38:
x: [36.000 36.000]
P: [0.000 -1.000]
u: [1.800 -6.891]
Elements:
---------------------
Truss: Node_36 to Node_37:
material properties: FiberMaterial(Material)({'E': 10.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30}) strain:0.04999999999999999 stress:{'xx': np.float64(0.4999999999999999), 'yy': 0.0, 'zz': 0.0, 'xy': 0.0}
internal force: 0.4999999999999999
Truss: Node_36 to Node_38:
material properties: FiberMaterial(Material)({'E': 10.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30}) strain:-0.07071067811865474 stress:{'xx': np.float64(-0.7071067811865474), 'yy': 0.0, 'zz': 0.0, 'xy': 0.0}
internal force: -0.7071067811865474
Truss: Node_37 to Node_38:
material properties: FiberMaterial(Material)({'E': 10.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30}) strain:-0.07071067811865472 stress:{'xx': np.float64(-0.7071067811865472), 'yy': 0.0, 'zz': 0.0, 'xy': 0.0}
internal force: -0.7071067811865472
System Analysis Report
=======================
Nodes:
---------------------
Node_36:
x: [0.000 0.000]
fix: ['ux', 'uy']
u: [0.000 0.000]
Node_37:
x: [72.000 0.000]
fix: ['uy', 'ux']
u: [0.000 0.000]
Node_38:
x: [36.000 36.000]
P: [0.000 -1.000]
u: [0.000 -5.091]
Elements:
---------------------
Truss: Node_36 to Node_37:
material properties: FiberMaterial(Material)({'E': 10.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30}) strain:0.0 stress:{'xx': np.float64(0.0), 'yy': 0.0, 'zz': 0.0, 'xy': 0.0}
internal force: 0.0
Truss: Node_36 to Node_38:
material properties: FiberMaterial(Material)({'E': 10.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30}) strain:-0.07071067811865472 stress:{'xx': np.float64(-0.7071067811865472), 'yy': 0.0, 'zz': 0.0, 'xy': 0.0}
internal force: -0.7071067811865472
Truss: Node_37 to Node_38:
material properties: FiberMaterial(Material)({'E': 10.0, 'A': 1.0, 'nu': 0.0, 'fy': 1e+30}) strain:-0.07071067811865472 stress:{'xx': np.float64(-0.7071067811865472), 'yy': 0.0, 'zz': 0.0, 'xy': 0.0}
internal force: -0.7071067811865472
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.039 seconds)